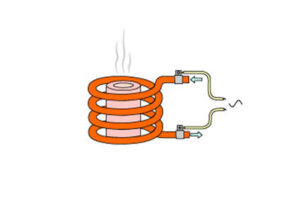
 Induction furnaces use induction to heat metal to its melting point. Most induction furnaces consist of a tube of water-cooled copper rings surrounding a container of refractory material. Induction furnaces are used in most modern foundries as a cleaner method of melting metals. Metals melted include iron and steel alloys, copper, aluminium, and precious metals as well as products for semiconductor manufacture.
Induction furnaces use induction to heat metal to its melting point. Most induction furnaces consist of a tube of water-cooled copper rings surrounding a container of refractory material. Induction furnaces are used in most modern foundries as a cleaner method of melting metals. Metals melted include iron and steel alloys, copper, aluminium, and precious metals as well as products for semiconductor manufacture.
Because it is a clean and non-contact process induction melting can be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere. Vacuum furnaces make use of induction heating for the production of speciality steels and other alloys that would oxidize if heated in the presence of air.
An important feature of the induction heating process is that the heat is generated inside the object itself, instead of by an external heat source via heat conduction. Thus objects can be heated very rapidly using the right form of ceramic for containment.
Ceramic and Refractory materials are used extensively in both the furnace construction (Electrical and thermal insulation and the coil grout to protect the coil should there be a spill) and in the Containment, Filtration and transfer of the molten metal and also in the final casting moulds as support structures for the mould.
Anderman Industrial Ceramics supplies a wide range of ceramic and refractory pre-formed shapes and castables to induction furnace applications for both furnace construction and consumables used in materials melting in both vacuum and air applications.
For further product information please visit the pages linked below.